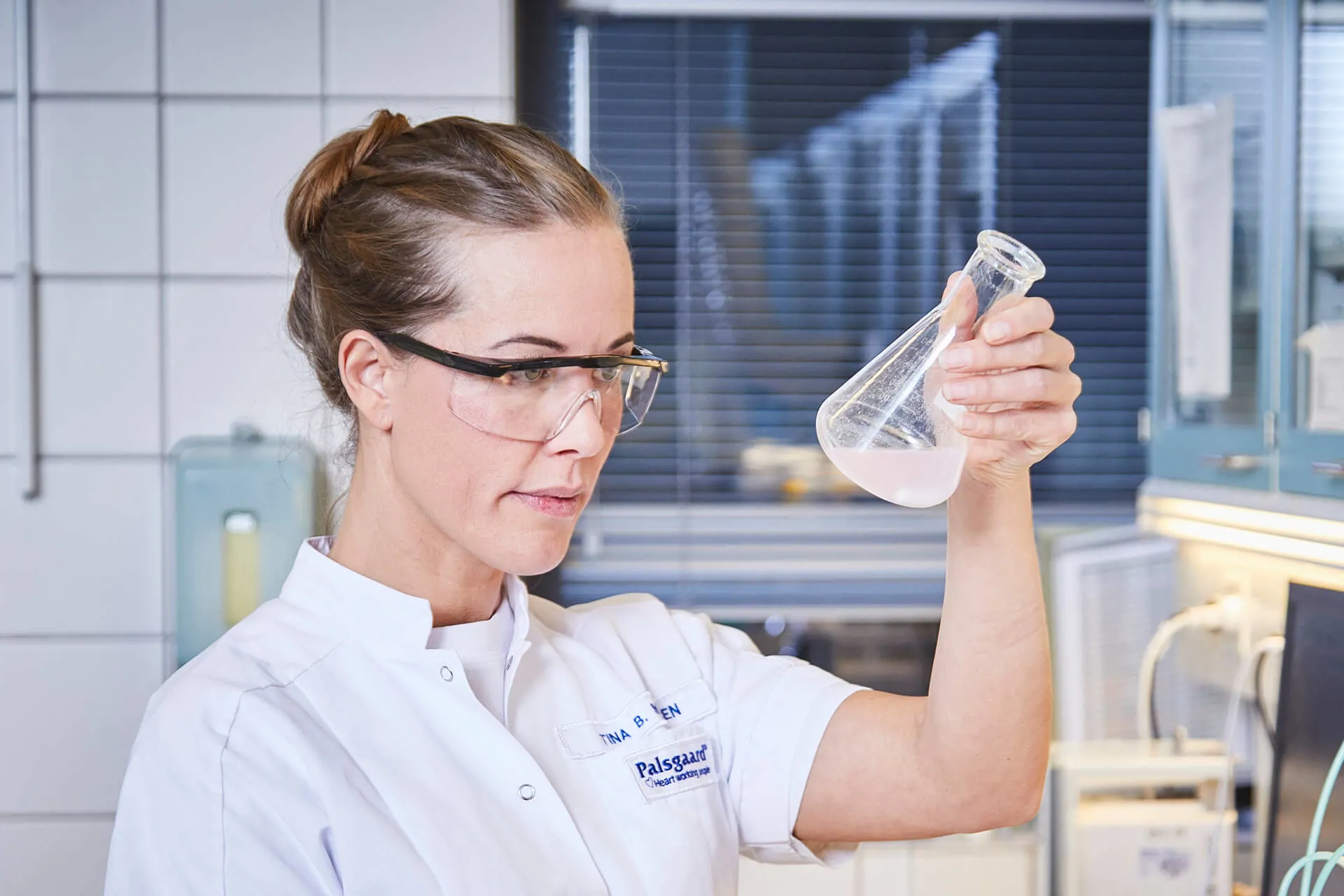

Safeguarding Food Integrity: Tackling Fraud Through FSSC 22000 Compliance
Food fraud refers to cases in which the intentional tampering of food is committed for economic gain. An example is when a liquid is diluted with water without appropriate labelling by the producer.
The prevention of food fraud has been formalised in the latest version of the FSSC 22000 standard. Companies are required to develop a risk analysis process to identify if they are vulnerable to food fraud. Our Global QEHS department is working alongside Global Procurement and Global Regulatory Affairs to address this additional requirement for certification across all our production sites.
Rigorous Quality Control
We currently have measures in place to detect food fraud, if present. The quality control of raw materials involves a range of highly specialised and detailed analyses. This ensures that each delivery meets the specifications for identity, physical form, chemical purity and functionality.
Our finished products also undergo an intensive process before being released for distribution. They are analysed in a positive release system, which checks compliance of functional performance parameters and chemical specifications defined for the product.
Read more about our CSR activities here


RESPONSIBLE PRODUCTION
Responsible Resource Consumption

RESPONSIBLE PRODUCTS
RSPO-certified Products

RESPONSIBLE PRODUCTS
Non-palm Food Emulsifiers, Personal Care Ingredients and Polymer Additives

RESPONSIBLE COMPANY
Corporate Governance

RESPONSIBLE COMPANY
Anti-bribery and Corruption

RESPONSIBLE COMPANY
Responsible Sourcing Programme

RESPONSIBLE COMPANY
Human Rights

RESPONSIBILITY
UN Sustainable Development Goals

RESPONSIBLE COMPANY
